RABBIT Health Information
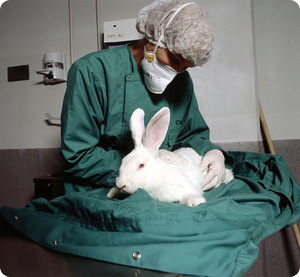
RABBIT Medicine Information
Rabbits do not like taking medications, nor do they like being restrained when given medication. Always try gently feeding the medication to your rabbit before trying to follow these steps below. To reduce excess stress on your rabbit, work quickly to administer the medication.
Liquid Medication
Liquid medication is best given by using a syringe or eye dropper to draw up the required amount of medication.
Hold the rabbit’s head and neck with one hand and use the other hand to insert the tip of the syringe or eyedropper behind the front teeth.
When the rabbit opens its mouth to try and spit out the syringe, slowly administer the medication into its mouth.
Tablet Medication
Pills should be crushed before they are given to rabbits.
Mix the crushed pill with ¼ teaspoon (1ml) of flavored Sustacal or Ensure.
Use a syringe or eyedropper, as described above, to administer the liquid.
For treating specific types of parasites and other diseases, sometimes injection medications may be necessary. Injecting medication should always be done by a trained professional - most often your local veterinarian.
RABBIT Vaccinations
Rabbits are highly susceptible to myxomatosis, a severe viral infection transmitted by mosquitoes and other biting insects. Infected rabbits can die within hours of contracting the virus and therefore vaccination is really the only method of protection.
Rabbits should be vaccinated once they are six weeks old
The vaccine is not a form of treatment in infected rabbits
Pregnant rabbits should not be vaccinated
Rabbits will not be fully immune until 14 days following the vaccination
Booster shots are recommended annually
RABBIT Emergencies
When faced with life threatening illnesses, rabbits will require veterinary care with in hours of the first symptoms. Do not delay in seeking medical help for your rabbit if it exhibits any of the following sypmptoms:
Uncontrollable bleeding – from self induced injuries or if attacked by a predator.
Broken bones – including injuries caused from falling
Extreme drop in body temperature – including shock caused by being drenched with water
Severe Diarrhea
Difficulty breathing or labored breathing
Blood present in urine – orange or red colored urine
Poisoning – look for signs of temporary paralysis
| |
Other Categories
RABBIT Pet Care
RABBIT Health Information
RABBIT Diseases
RABBIT Kits
RABBIT Products
Main Categories
DOGS
CATS
HORSES
BIRDS
RABBITS
HAMSTERS
MICE AND RATS
GUINEA PIGS
FISH
|

